Create containers
CI Pipeline
Section titled “CI Pipeline”Continuous Integration is a pipeline which consists of steps required to create a packaged artifact which can then be used to run an application.
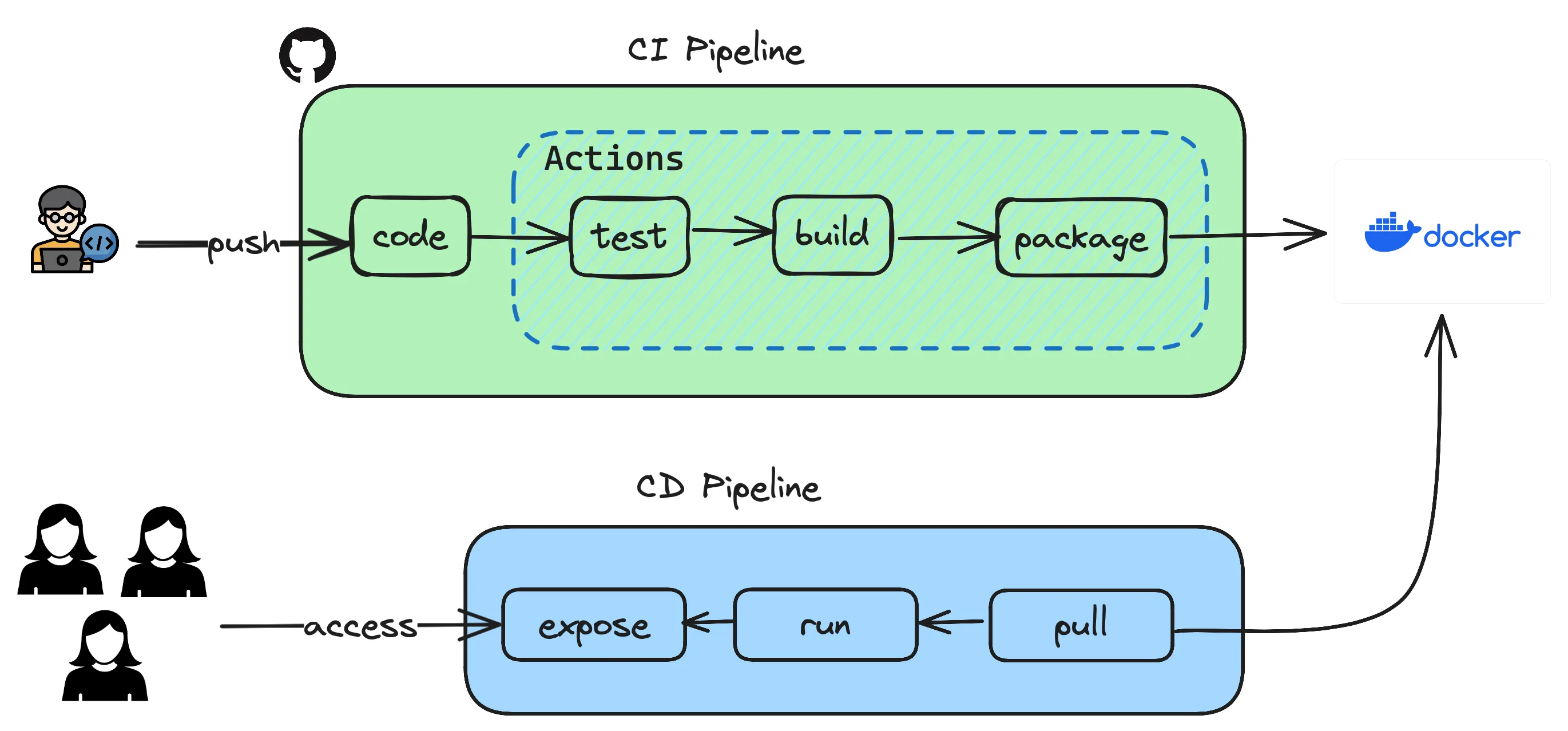
Previously you have created an API using springboot and have executed steps manually which resulted in testing, building and packaging as a container to be used. Let’s see how those steps can be automated so that it all happens in a click of button or even better when pushing a code to repository.
- Open the GitHub repository and goto your repo which contains the Java application using springboot.
- Goto
Settingstab andSecuritysection where you can seeSecrets and Variablesand click on Actions. - Based on the pipeline depicted above, the only external integration you have is to use Docker where you maintain the container images which are built using
Dockerfileyou already have. - You create two variables
DOCKERHUB_TOKENandDOCKERHUB_USERNAMEas secrets so that you dont have to hardcode these secrets in your sourcecode. - In order to get the
DOCKERHUB_TOKENyou login to your DockerHub. GotoMyAccount->Securityand then createNew Access Tokenwith permissionsRead & Write. This will give the token access to read and write to your repository in DockerHub. - Copy the token and create the GitHub Secret
DOCKERHUB_TOKEN - For
DOCKERHUB_USERNAME, use your login username. - Once the secrets are created, GitHub Actions now has the permission to write the images to your repository. You will use these values in your workflow.
- Either from your local laptop or any terminal create the following directory structure and files and copy paste the code given below to your
maven.yml
.github└── workflows └── maven.yml# This workflow will build a Java project with Maven, and cache/restore any dependencies to improve the workflow execution time
name: Java CI with Maven
on: push: branches: [ "main" ] pull_request: branches: [ "main" ]
jobs: build: runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - uses: actions/checkout@v3 - name: Set up JDK 17 uses: actions/setup-java@v3 with: java-version: '17' distribution: 'temurin' cache: maven - name: Run unit test cases run: mvn test - name: Build the jar file run: mvn package - name: Set up QEMU uses: docker/setup-qemu-action@v3 - name: Set up Docker Buildx uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3 - name: Login to Docker Hub uses: docker/login-action@v3 with: username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }} password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_TOKEN }} - name: Build and push uses: docker/build-push-action@v5 with: context: . push: true tags: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}/spring-rest-api:latest- Now you commit your changes
git add . && git commit -m "added github actions"and pushgit pushthis to your repository. Once the change is pushed goto yourActionstab on the repository and see the magic happening.
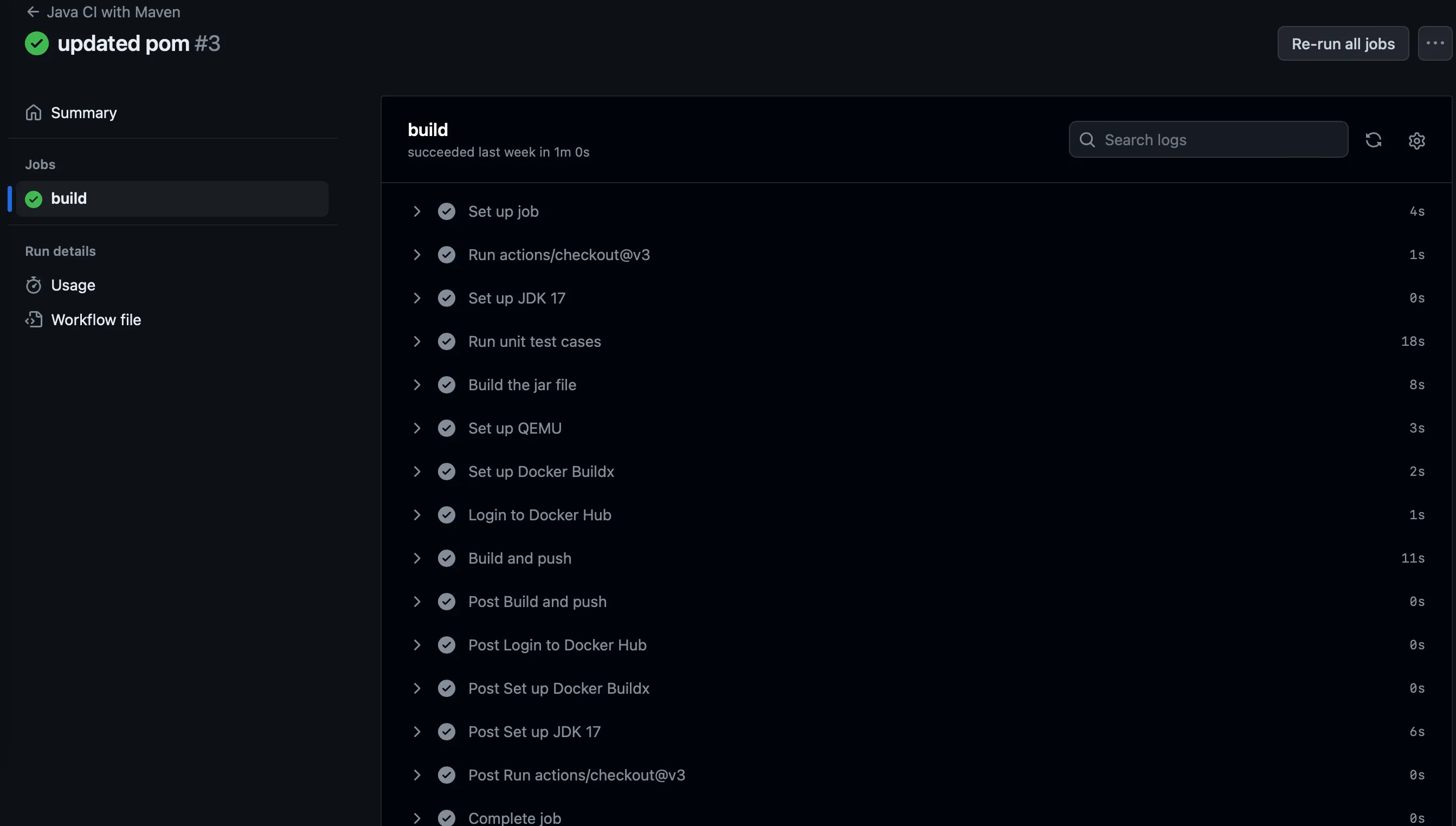
Everytime you push a code to main branch, the build will be triggered and new version of image will be pushed to docker hub.
